Menstrual Cycle
Menstrual cycle overview
- The menstrual cycle is the term for changes a woman’s body goes through to prepare for a potential pregnancy each month.
- Most women have their first period, or menarche, between the ages of 11 and 14, and have regular menstrual cycles until about age 50.
- The menstrual cycle typically lasts about 28 days; however, it is normal to have a cycle that is a few days shorter or longer.
- The days of a menstrual cycle are counted from Day 1 of menstrual bleeding to Day 1 of the next menstrual bleeding.
What is a menstrual cycle?
The menstrual cycle is the process by which a woman’s body prepares for pregnancy. Once a month, the female body grows a new uterine lining (endometrium) that is ready to receive and nourish a fertilized egg. If an egg is not fertilized, the uterus sheds the endometrium and a woman experiences menstrual bleeding, or her period.
Most women have their first period, or menarche, between the ages of 10-16 and have regular menstrual cycles until about age 50. The menstrual cycle typically lasts about 28 days; however, it is normal to have a cycle that is a few days shorter or longer.
The days of a menstrual cycle are counted from Day 1 of menstrual bleeding to Day 1 of the next menstrual bleeding.
The menstrual cycle is guided by hormonal signals sent by the brain. Estrogen causes the uterine lining to develop and thicken; follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates the development and release of a mature egg; and progesterone levels increase in order to help a fertilized egg attach to the uterine lining.
Menstrual cycle timeline
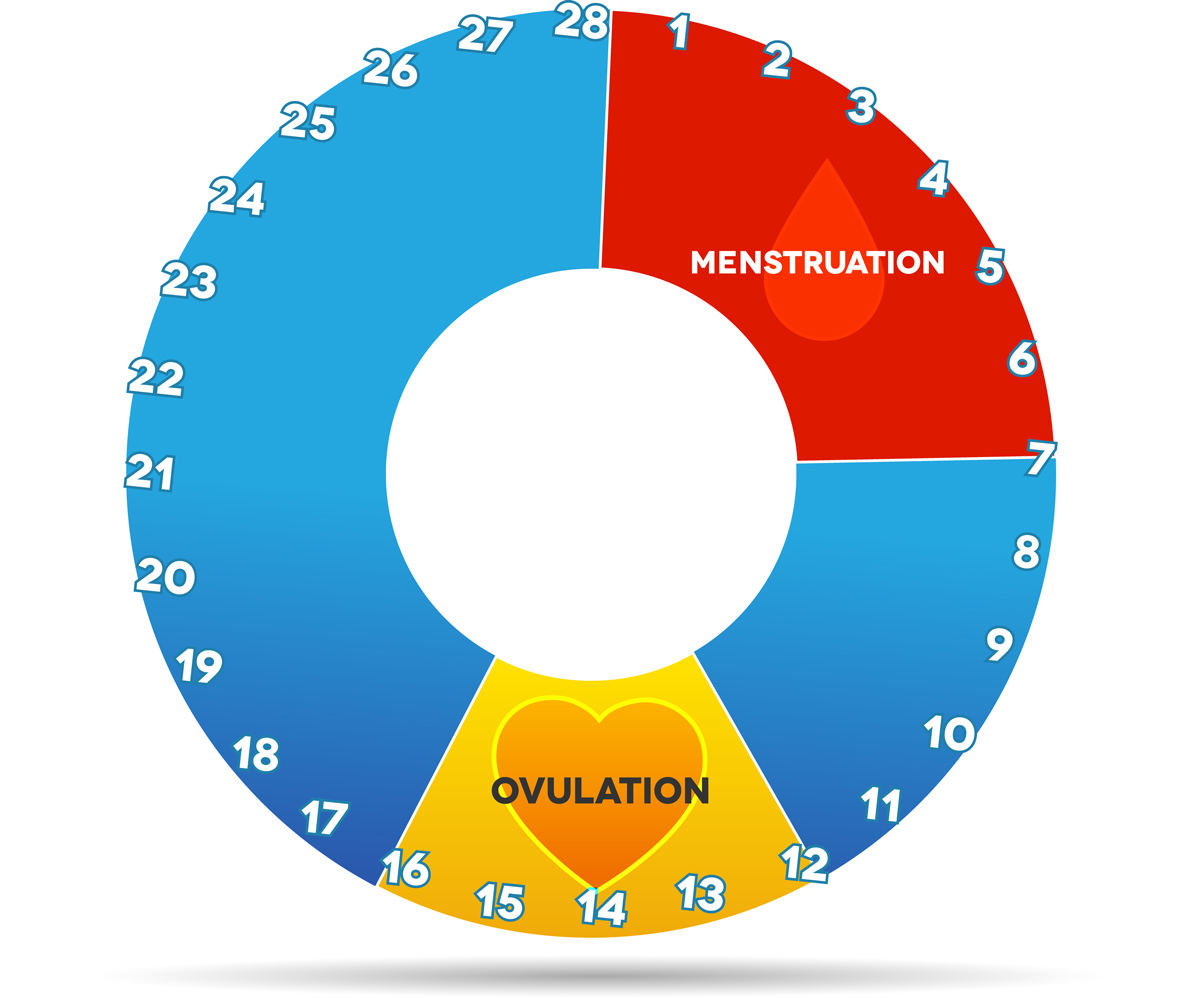
- Days 1-5: Menses phase – bleeding occurs
- Days 6-14: Follicular phase – an egg matures in the ovarian follicle, and the uterine lining prepares to receive a fertilized egg (embryo)
- Day 14: Ovulation – the ovary releases the egg, which can be fertilized by a man’s sperm if present
- Days 15-28: Luteal phase – the egg travels through the fallopian tubes to the uterus; if fertilized, the embryo may attach to the uterine lining and the woman will become pregnant; if the egg is not fertilized, the uterine lining will shed and the cycle will begin again.
Common menstrual problems
Most women can predict their menstrual cycle due to its regularity, however, there are a few common problems that can affect the cycle:
- Amenorrhea – lack of menstrual cycle
- Dysmenorrhea – painful periods
- Abnormal uterine bleeding.
Amenorrhea
Amenorrhea is a term used to describe the condition of women who haven’t gotten their period by age 15 or women who haven’t had a period for more than 90 days. The most common cause of amenorrhea is pregnancy.
Other causes of amenorrhea are:
- Breastfeeding
- Extreme weight loss
- Obesity
- Eating disorders
- Excessive exercise
- Stress
- Medical conditions in need of treatment.
Dysmenorrhea
Dysmenorrhea is a condition in which a woman experiences painful menses, usually in the form of abdominal cramps during her period. It is most often caused by an excess of the chemical prostaglandin, a hormone that helps the body heal after injury. The symptoms of pain and discomfort caused by dysmenorrhea can be relieved by over-the-counter medication, such as ibuprofen, Advil, Motrin or Midol. If pain persists and interrupts a normal routine, treatment from a doctor is recommended.
Abnormal uterine bleeding
Abnormal uterine bleeding occurs when a woman experiences bleeding in the middle of her menstrual cycle or experiences excessive bleeding during her period. Abnormal bleeding can happen:
- After sex
- Between periods
- After menopause.
Abnormal uterine bleeding by itself may not indicate a serious medical condition. Many times, women can bleed from ovulation or birth control medication and devices. However, abnormal bleeding may also indicate an underlying condition that could be causing infertility. Women experiencing abnormal bleeding should see their doctor to confirm a diagnosis.
