In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
IVF overview
- The in vitro fertilization (IVF) technique combines a man’s sperm and a woman’s eggs outside the woman’s body in a lab where fertilization occurs.
- Generally, one fertilized egg (an embryo) is then placed in the woman’s uterus, where it can result in a successful pregnancy and birth.
- IVF has the highest success rate of all fertility treatments, averaging more than 1 in 3 successful pregnancies, with even better pregnancy rates for younger women.
- IVF is used to address a wide range of fertility problems, including male and female infertility conditions.
What is IVF?
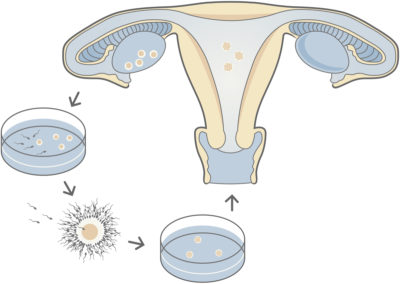 “In vitro” means in glass and describes studies and procedures that are performed outside the body in a glass laboratory dish or container. In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a technique that collects a woman’s eggs and a man’s sperm to combine them in a fertility clinic laboratory for fertilization. Once the fertilized egg, called an embryo, is created, it is transferred to the woman’s uterus where it can implant and create a pregnancy.
“In vitro” means in glass and describes studies and procedures that are performed outside the body in a glass laboratory dish or container. In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a technique that collects a woman’s eggs and a man’s sperm to combine them in a fertility clinic laboratory for fertilization. Once the fertilized egg, called an embryo, is created, it is transferred to the woman’s uterus where it can implant and create a pregnancy.
During egg retrieval, medications are often used to stimulate increased mature egg production to increase chances of creating healthy embryos. Sperm retrieval can be achieved naturally or through surgical procedures in certain cases of male infertility. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) is often used in conjunction with IVF for fertilization in cases of male infertility.
Once the embryos have been created, patients can choose to have genetic testing performed to rule out any health problems before the embryo is transferred into the woman’s uterus.
Fertility doctors utilize IVF treatments to overcome many causes of infertility, both male and female. The first “IVF baby” was born in 1978, and since then, more than four million IVF babies have been born worldwide.
IVF success rates
IVF success depends on many factors that vary from individual to individual. Each attempt at pregnancy through IVF is known as a cycle. IVF can be tried more than once if the first attempt is not successful. A cycle can be fresh (the woman’s eggs are collected, fertilized and the embryo is transferred within the same menstrual cycle) or frozen (the collected eggs are fertilized and the embryos are frozen for transfer during a future cycle).
IVF has the highest success rate of all fertility treatments, with even better pregnancy rates for younger women.
About single embryo transfer
One embryo is generally implanted during an IVF cycle, which is a recent and significant advancement in IVF. A single embryo transfer, called elective single embryo transfer (eSET), is now the preferred method, as implanting more than one embryo increases the prospect of multiple births (twins, triplets or more) and the associated risk of health problems for mother and child.
Genetic testing and IVF
Genetic testing can evaluate embryos for genetic disorders before uterus implantation. This is done with either preimplantation genetic screening (PGT-A) that tests for multiple genetic problems or preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGT-M) that tests for a specific genetic problem experienced in the male’s or female’s families.
What conditions can IVF treat?
IVF is the first-line treatment for women with fallopian tube abnormalities and for couples whose male partner has poor sperm quality. It is the second-line treatment for male- and female-related infertility problems not corrected by other treatments.
Due to its laboratory-based nature, IVF allows for the options of female egg donation and male sperm donation. These can enable couples and individuals whose fertility issues include problems with their own sperm or eggs to achieve pregnancy.
IVF is used to treat the following conditions, often after other measures have been tried.
Age-related infertility
Age-related infertility is due to the reduced quality of a woman’s eggs as she ages. IVF allows a reproductive endocrinologist to collect healthy eggs for fertilization or allows the patient to use donor eggs to create embryos.
Anovulation
Anovulation is a condition in which a woman fails to ovulate. IVF allows the doctor to stimulate ovulation and collect eggs for fertilization.
Damaged or blocked fallopian tubes
Damaged or blocked fallopian tubes can make it difficult or impossible for the sperm to reach the egg and the resulting embryo to reach the uterus. By collecting eggs and fertilizing them in the lab, IVF allows the fertilization process to bypass the fallopian tubes.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis occurs when tissue lining the inside of the uterus spreads to the outside, making pregnancy difficult. By taking much of the fertilization process out of the body and into the lab, IVF has a higher pregnancy success rate than normal conception for women with endometriosis.
Low ovarian reserve
When a woman has a low number of eggs in her ovaries, she has low ovarian reserve. The IVF process stimulates healthy eggs to develop, allowing the reproductive endocrinologist to collect mature eggs directly from the ovaries.
Male factor infertility
Male factor infertility, which generally involve issues with sperm health. IVF is often used in conjunction with intracytoplasmic sperm in injection (ICSI) using the man’s sperm to ensure fertilization.
What are the risks of IVF?
The IVF procedure involves several elements, each of which can carry some risk. The American Society for Reproductive Medicine reports that serious complications from IVF procedures or medications are rare.
Fertility drug side effects
These may occur, as women take ovulation induction medications to stimulate production of eggs for retrieval. Side effects of these drugs can include soreness at the injection site, mood alterations, gastrointestinal upset, headache and allergic reactions.
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS)
This condition may also result from IVF medications. Moderate OHSS involving swelling and pain is common. Extreme OHSS can include symptoms of vomiting, nausea, bloated feeling and poor appetite. More severe symptoms would involve considerable abdominal pain, shortness of breath, decreased urination frequency or a 10-pound weight gain over 3-5 days. In severe cases of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, the IVF cycle may need to be postponed or cancelled to allow the woman to recover.
Risks with egg retrieval
Egg retrieval is performed by an ultrasound-guided needle through the vaginal wall, and carries risks of internal bleeding, issues associated with anesthesia, and infection and damage to bladder, bowel or blood vessels.
Risks with embryo transfer
An embryo transfer involves a catheter and may cause spot bleeding, cramps and infection.
Multiple pregnancy
A multiple pregnancy, twins or more, may occur if more than one embryo is implanted. This can involve pregnancy and labor complications, premature delivery and ongoing medical and developmental problems for the children.
Psychological stress
Stress and emotional problems can accompany IVF treatment, as it involves physical and financial commitments of individuals and couples, and can even extend to their family members and friends. Counselors can help IVF patients manage stress and may advise massage, acupuncture, yoga or meditation.
